Understand Heel Pain
Overview

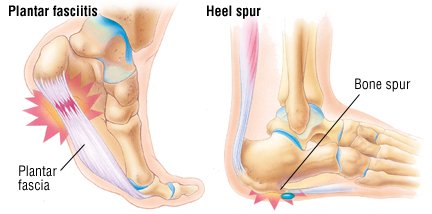
The most common cause of heel pain is plantar fasciitis which is commonly referred to as a heel spur. Plantar fascia is a broad band of fibrous tissue which runs along the bottom surface of the foot, from the heel to the toes. Plantar fasciitis is a condition in which the plantar fascia is inflamed. This condition can be very painful and cause a considerable amount of suffering.
Causes
Plantar fasciitis can come from a number of underlying causes. Finding the precise reason for the heel pain is sometimes difficult. As you can imagine, when the foot is on the ground a tremendous amount of force (the full weight of the body) is concentrated on the plantar fascia. This force stretches the plantar fascia as the arch of the foot tries to flatten from the weight of your body. This is just how the string on a bow is stretched by the force of the bow trying to straighten. This leads to stress on the plantar fascia where it attaches to the heel bone. Small tears of the fascia can result. These tears are normally repaired by the body. As this process of injury and repair repeats itself over and over again, a bone spur (a pointed outgrowth of the bone) sometimes forms as the body's response to try to firmly attach the fascia to the heelbone. This appears on an X-ray of the foot as a heel spur. Bone spurs occur along with plantar fasciitis but they are not the cause of the problem. As we age, the very important fat pad that makes up the fleshy portion of the heel becomes thinner and degenerates (starts to break down). This can lead to inadequate padding on the heel. With less of a protective pad on the heel, there is a reduced amount of shock absorption. These are additional factors that might lead to plantar fasciitis. Some physicians feel that the small nerves that travel under the plantar fascia on their way to the forefoot become irritated and may contribute to the pain. But some studies have been able to show that pain from compression of the nerve is different from plantar fasciitis pain. In many cases, the actual source of the painful heel may not be defined clearly. Other factors that may contribute to the development of plantar fasciitis include obesity, trauma, weak plantar flexor muscles, excessive foot pronation (flat foot) or other alignment problems in the foot and or ankle, and poor footwear.
Symptoms
Symptoms of plantar fasciitis vary, but the classic symptom is pain after rest--when you first get out of bed in the morning, or when you get up after sitting down for a while during the day. The pain usually diminishes after a few minutes of walking, sometimes even disappearing, but the pain is commonly felt again the longer you're on the foot. Fasciitis can be aggravated by shoes that lack appropriate support, especially in the arch area, and by the chronic irritation of long-periods of standing, especially on concrete, by being overweight. It doesn't help that fascia doesn't heal particularly quickly because it has relatively poor circulation (which is why it's white in colour).
Diagnosis
Your doctor will perform a physical exam and ask questions about your medical history and symptoms, such as have you had this type of heel pain before? When did your pain begin? Do you have pain upon your first steps in the morning or after your first steps after rest? Is the pain dull and aching or sharp and stabbing? Is it worse after exercise? Is it worse when standing? Did you fall or twist your ankle recently? Are you a runner? If so, how far and how often do you run? Do you walk or stand for long periods of time? What kind of shoes do you wear? Do you have any other symptoms? Your doctor may order a foot x-ray. You may need to see a physical therapist to learn exercises to stretch and strengthen your foot. Your doctor may recommend a night splint to help stretch your foot. Surgery may be recommended in some cases.
Non Surgical Treatment
If you develop heel pain, you can try several methods at home to ease your discomfort. For example rest as much as possible, apply ice to the heel for 10 to 15 minutes twice a day, use over-the-counter pain medications, wear shoes that fit properly, wear night splints, a special device that stretches the foot while you sleep, use heel cups or shoe inserts to reduce pain, If these home care strategies do not ease your pain, you will need to see your doctor. He or she will perform a physical exam and ask you about your symptoms and when they began. Your doctor may also take an X-ray to determine the cause of your heel pain. Once your doctor knows what is causing your pain, he or she will be able to provide you with the appropriate treatment. In many cases, your doctor may prescribe physical therapy. This can help to strengthen the muscles and tendons in your foot, which helps to prevent further injury. If your pain is severe, your doctor may provide you with anti-inflammatory medications. These medications can be injected into the foot or taken by mouth. Your doctor may also recommend that you support your foot as much as possible-either by taping the foot or by using special footwear devices. In very rare cases, your doctor may recommend surgery to correct the problem. However, heel surgery often requires a long recovery time and may not always relieve your foot pain.
Surgical Treatment
Only a relatively few cases of heel pain require surgery. If required, surgery is usually for the removal of a spur, but also may involve release of the plantar fascia, removal of a bursa, or a removal of a neuroma or other soft-tissue growth.
bestshoelifts
Prevention
It is not always possible to prevent heel pain, but there are measures you can take to help avoid further episodes. Being overweight can place excess pressure and strain on your feet, particularly on your heels. This increases the risk of damaging your feet and heels. If you are overweight, losing weight and maintaining a healthy weight by combining regular exercise with a healthy, balanced diet can be beneficial for your feet. You can calculate your body mass index (BMI) to find out whether you are a healthy weight for your height and build. To work out your BMI, divide your weight in kilograms by your height in metres squared. A BMI of less than 18.5 means that you are underweight, 18.5-24.9 means that your weight is healthy, 25-29 means that you are overweight, 30-40 means that you are obese, over 40 means that you are morbidly obese. You can also use the BMI healthy weight calculator to work out your BMI.

The most common cause of heel pain is plantar fasciitis which is commonly referred to as a heel spur. Plantar fascia is a broad band of fibrous tissue which runs along the bottom surface of the foot, from the heel to the toes. Plantar fasciitis is a condition in which the plantar fascia is inflamed. This condition can be very painful and cause a considerable amount of suffering.
Causes
Plantar fasciitis can come from a number of underlying causes. Finding the precise reason for the heel pain is sometimes difficult. As you can imagine, when the foot is on the ground a tremendous amount of force (the full weight of the body) is concentrated on the plantar fascia. This force stretches the plantar fascia as the arch of the foot tries to flatten from the weight of your body. This is just how the string on a bow is stretched by the force of the bow trying to straighten. This leads to stress on the plantar fascia where it attaches to the heel bone. Small tears of the fascia can result. These tears are normally repaired by the body. As this process of injury and repair repeats itself over and over again, a bone spur (a pointed outgrowth of the bone) sometimes forms as the body's response to try to firmly attach the fascia to the heelbone. This appears on an X-ray of the foot as a heel spur. Bone spurs occur along with plantar fasciitis but they are not the cause of the problem. As we age, the very important fat pad that makes up the fleshy portion of the heel becomes thinner and degenerates (starts to break down). This can lead to inadequate padding on the heel. With less of a protective pad on the heel, there is a reduced amount of shock absorption. These are additional factors that might lead to plantar fasciitis. Some physicians feel that the small nerves that travel under the plantar fascia on their way to the forefoot become irritated and may contribute to the pain. But some studies have been able to show that pain from compression of the nerve is different from plantar fasciitis pain. In many cases, the actual source of the painful heel may not be defined clearly. Other factors that may contribute to the development of plantar fasciitis include obesity, trauma, weak plantar flexor muscles, excessive foot pronation (flat foot) or other alignment problems in the foot and or ankle, and poor footwear.
Symptoms
Symptoms of plantar fasciitis vary, but the classic symptom is pain after rest--when you first get out of bed in the morning, or when you get up after sitting down for a while during the day. The pain usually diminishes after a few minutes of walking, sometimes even disappearing, but the pain is commonly felt again the longer you're on the foot. Fasciitis can be aggravated by shoes that lack appropriate support, especially in the arch area, and by the chronic irritation of long-periods of standing, especially on concrete, by being overweight. It doesn't help that fascia doesn't heal particularly quickly because it has relatively poor circulation (which is why it's white in colour).
Diagnosis
Your doctor will perform a physical exam and ask questions about your medical history and symptoms, such as have you had this type of heel pain before? When did your pain begin? Do you have pain upon your first steps in the morning or after your first steps after rest? Is the pain dull and aching or sharp and stabbing? Is it worse after exercise? Is it worse when standing? Did you fall or twist your ankle recently? Are you a runner? If so, how far and how often do you run? Do you walk or stand for long periods of time? What kind of shoes do you wear? Do you have any other symptoms? Your doctor may order a foot x-ray. You may need to see a physical therapist to learn exercises to stretch and strengthen your foot. Your doctor may recommend a night splint to help stretch your foot. Surgery may be recommended in some cases.
Non Surgical Treatment
If you develop heel pain, you can try several methods at home to ease your discomfort. For example rest as much as possible, apply ice to the heel for 10 to 15 minutes twice a day, use over-the-counter pain medications, wear shoes that fit properly, wear night splints, a special device that stretches the foot while you sleep, use heel cups or shoe inserts to reduce pain, If these home care strategies do not ease your pain, you will need to see your doctor. He or she will perform a physical exam and ask you about your symptoms and when they began. Your doctor may also take an X-ray to determine the cause of your heel pain. Once your doctor knows what is causing your pain, he or she will be able to provide you with the appropriate treatment. In many cases, your doctor may prescribe physical therapy. This can help to strengthen the muscles and tendons in your foot, which helps to prevent further injury. If your pain is severe, your doctor may provide you with anti-inflammatory medications. These medications can be injected into the foot or taken by mouth. Your doctor may also recommend that you support your foot as much as possible-either by taping the foot or by using special footwear devices. In very rare cases, your doctor may recommend surgery to correct the problem. However, heel surgery often requires a long recovery time and may not always relieve your foot pain.
Surgical Treatment
Only a relatively few cases of heel pain require surgery. If required, surgery is usually for the removal of a spur, but also may involve release of the plantar fascia, removal of a bursa, or a removal of a neuroma or other soft-tissue growth.
bestshoelifts
Prevention

It is not always possible to prevent heel pain, but there are measures you can take to help avoid further episodes. Being overweight can place excess pressure and strain on your feet, particularly on your heels. This increases the risk of damaging your feet and heels. If you are overweight, losing weight and maintaining a healthy weight by combining regular exercise with a healthy, balanced diet can be beneficial for your feet. You can calculate your body mass index (BMI) to find out whether you are a healthy weight for your height and build. To work out your BMI, divide your weight in kilograms by your height in metres squared. A BMI of less than 18.5 means that you are underweight, 18.5-24.9 means that your weight is healthy, 25-29 means that you are overweight, 30-40 means that you are obese, over 40 means that you are morbidly obese. You can also use the BMI healthy weight calculator to work out your BMI.